But what exactly are garden weeds?
Garden weeds are unwanted plants that naturally grow in yourlawn, flower beds, vegetable garden, and patio.
If you want to maintain pristinegreen outdoor spaces, youll have to keep the weeds at bay.

Share icon
Each weed has its unique characteristics, growth habits, and challenges.
How Many Types of Weeds Are There?
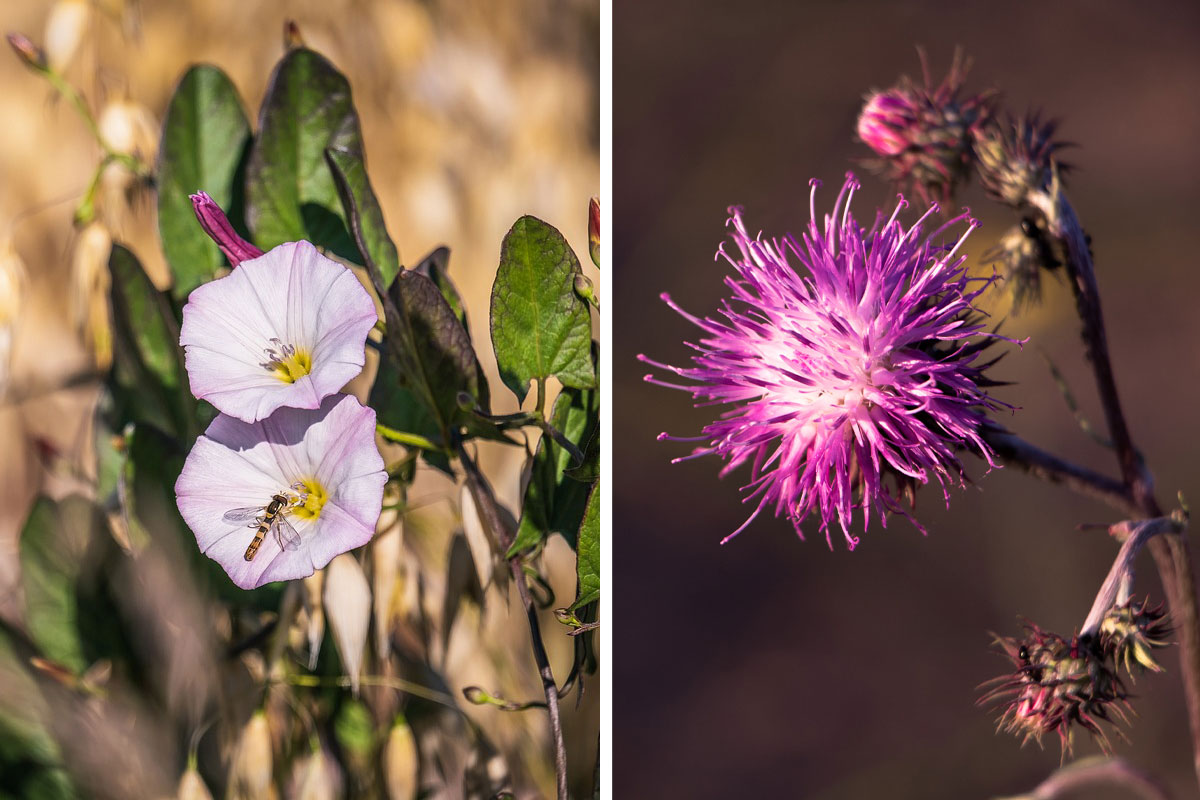
There are about30,000 speciesgrouped as weeds, and they can be classified based on their life cycle and morphology.

However, chemical weed control is usually the most effective.
Size:Up to 3 ft (90 cm) tall.
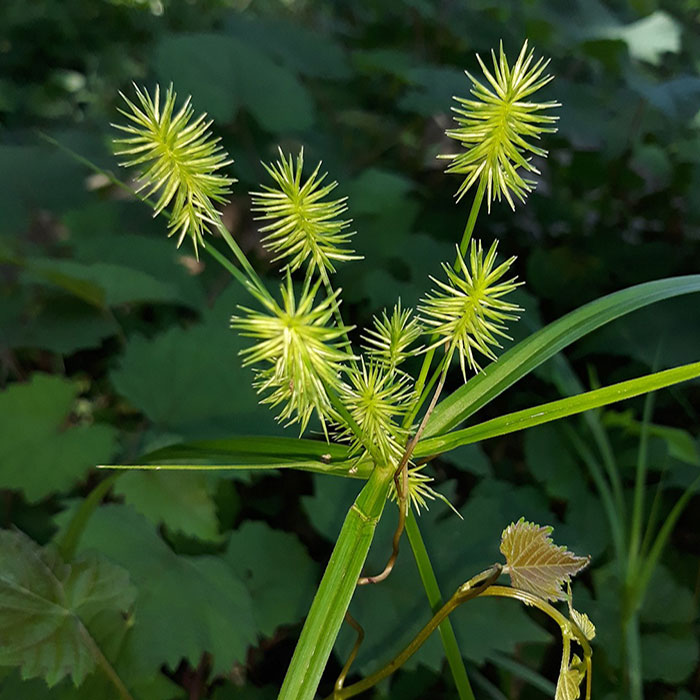
Tackling yellow nutsedge can be challenging since it grows fast and hides those pesky tubers underground.

Try pulling it out by hand, using mulch, and keeping your garden healthy to weaken it.
Size:About 2.5 ft (80 cm) tall.
At the ends of these stems, youll find clusters of spikelets that resemble finger-like structures.

Try using selective pre-emergent herbicides with active ingredients such asbensulide,dithiopyr,pendimethalin, andprodiaminein early spring.
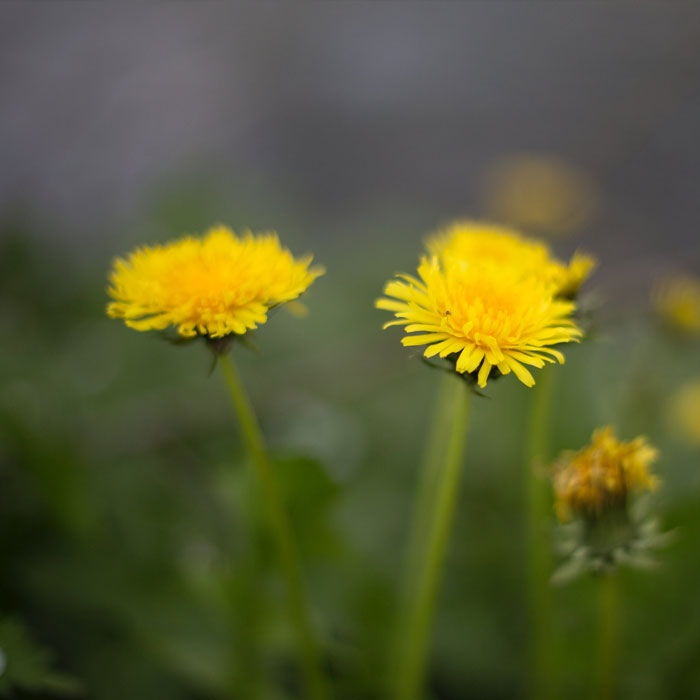
Beautiful spring-blooming dandelions can host aster yellow disease, which affects several vegetable crops.
Pull them out by hand, and keep your lawn healthy by mowing and mulching.

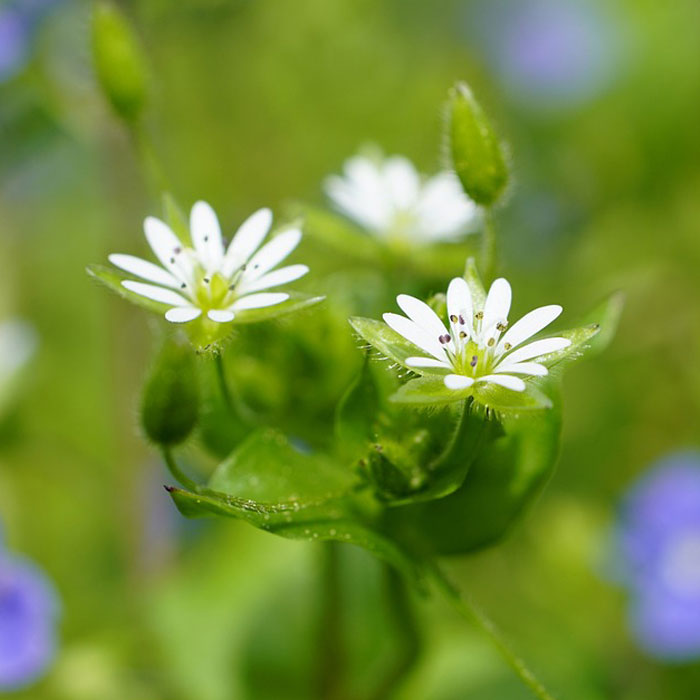
It blooms with tiny, star-shaped, white flowers, mainly from February to September.
Common chickweed can form dense mats that compete with turfgrass and other plants.
Size:1 to 5 ft (30 cm to 1,5 m) tall.

The leaves are deeply lobed and toothed, and the flowers are clustered at the end of the stems.
Size:Up to 4 ft (1.2 m) tall.
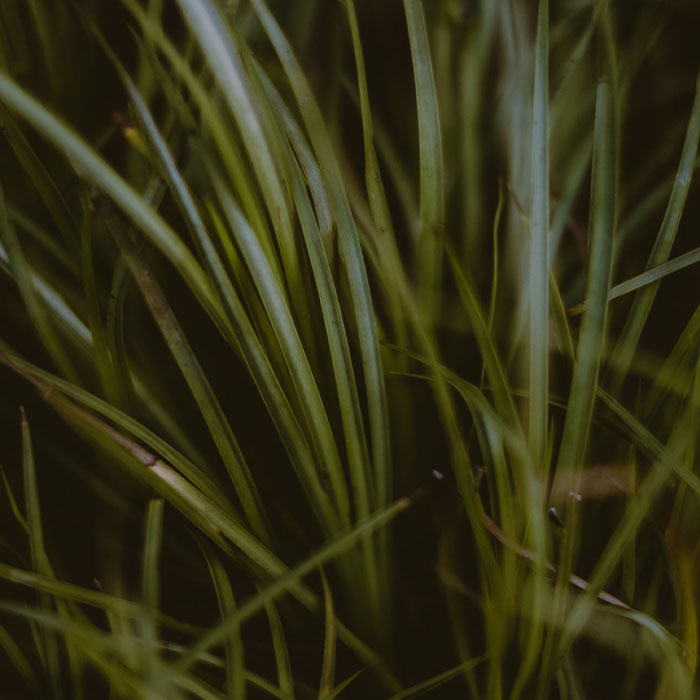
How to identify:Quackgrass has long, wide, lime-green blades with strongly ribbed veins.

The stems are hollow and grooved.
Quackgrass can compete with your desired plants.
To reduce its growth and seed production, remove it by hand-pulling, hoeing, or mowing.

Unfortunately, these methods wont remove the roots or wont do it entirely.
Try using non-selective herbicides with active ingredients such asglyphosatein spring or fall for more effective control.
Size:Up to 16 in (41 cm) tall.

Common purslane tends to form dense mats that compete with other plants.
Size:Up to 5 ft (1.8 m) tall.
How to identify:Redroot pigweed has a red, thick taproot and reddish, coarse, hairy stems.
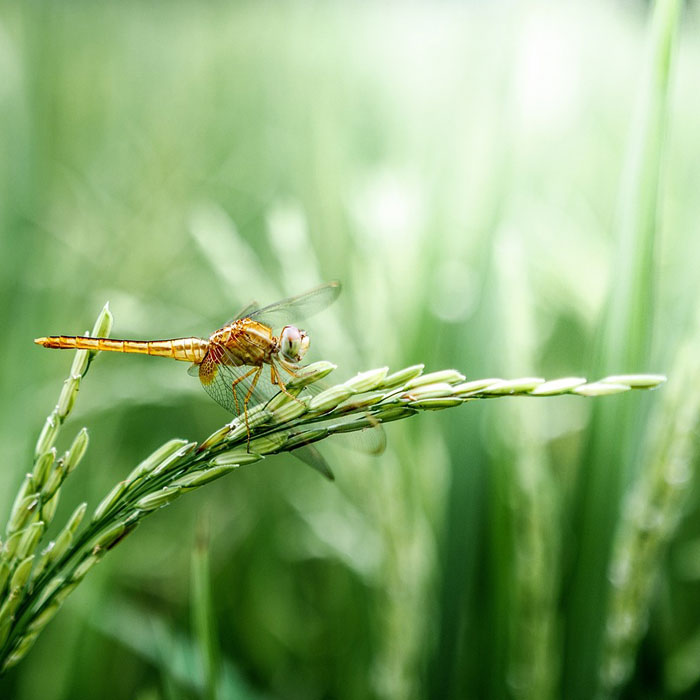

The leaves are oval to lance-shaped, with long petioles and prominent veins.
The flowers are green and clustered in dense spikes.
To control redroot pigweed, manually remove plants before flowering and seeds are produced.
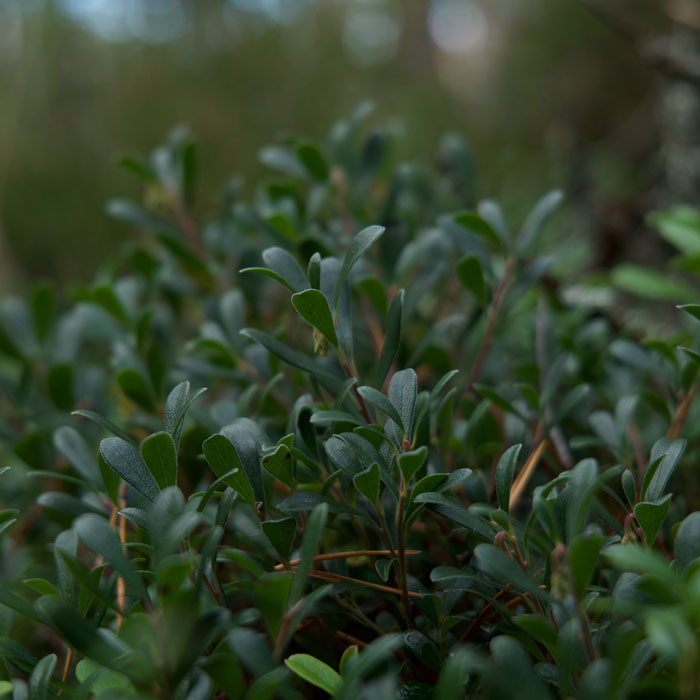

#9 White Clover(Trifolium repens)
Share iconImage credits:
throw in:Perennial weed.
Size:Up to 0.5 ft (15 cm) tall.
How to identify:The white clover leaves consist of three leaflets.

The plant bears clusters of pea-like flowers with a white tinge in half-inch flower heads.
To improve soil quality, consider removing it by hand, hoeing, mowing, and mulching.
Additionally, it’s possible for you to use pre- or post-emergence herbicides.

Size:2 to 20 in (5 to 50 cm) tall.
How to identify:Low, creepy plant with a distinct odor when crushed.
It has square stems with rounded, kidney-shaped leaves that grow opposite each other.
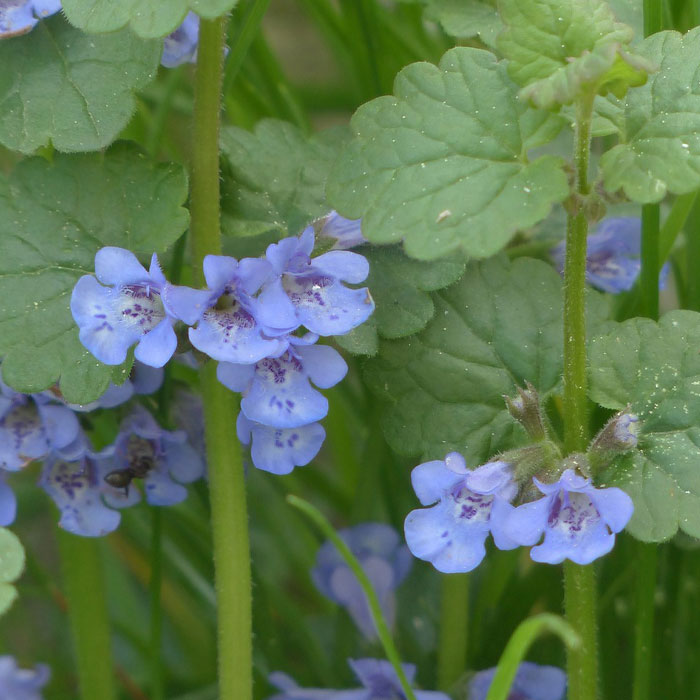

Ground-ivy can quickly spread and take over lawns and gardens.
To eradicate it, manually pull out the ground-ivy plants, ensuring the removal of the entire root system.
Size:About 1.5 ft (46 cm) tall.
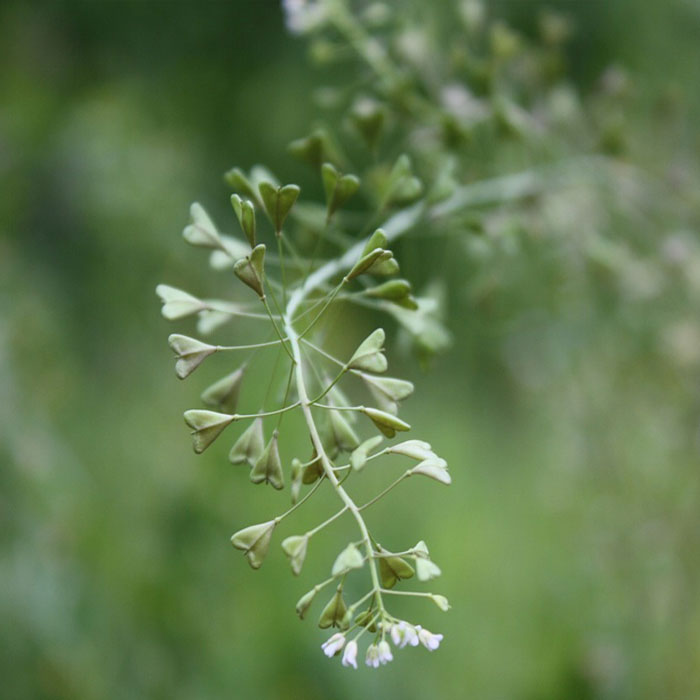

It has tiny, flat, triangular seed pods with a seam along the middle.
#12 Lambs Quarters(Chenopodium album)
punch in:Annual weed.
Size:Up to 6 ft (1.8 m) tall.
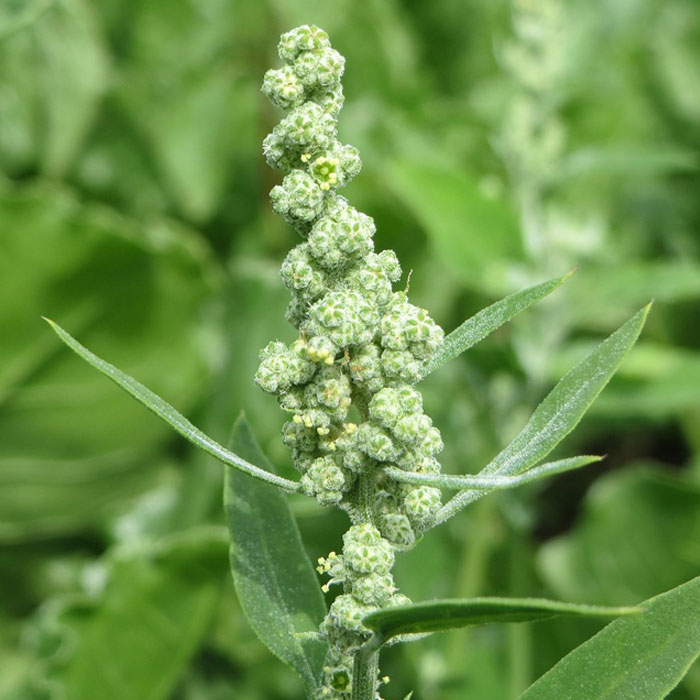

How to identify:The leaves are egg-shaped with irregular teeth and a whitish coating on the newest leaves.
The stem often displays vertical pink to red stripes.
The branched inflorescence bears small, radially symmetrical flowers arranged in small cymes.

To prevent flower production and seed formation, cultivate manually or employ regular mowing practices.
you’re able to also use selective broadleaf herbicidesthat contain2, 4-D, MCCP,ortriclopyr.
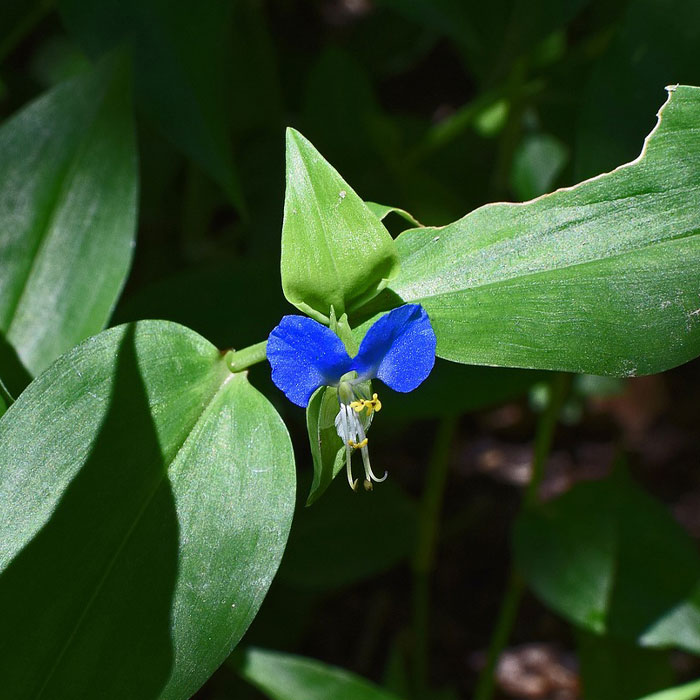
Size:1 to 2 ft (30 to 61 cm) tall.

Notably, these flowers only bloom for one day.
The leaves are hairless and broadly lance- to egg-shaped.
Before the plant grows large, remove all stem fragments by hand.

As the Asiatic dayflower loves moist soil, ensure good drainage to dry the soil.
If nothing helps, consider using pre- and early post-emergence herbicides that containflumioxazin.
#14 Common Blue Violet(Viola sororia)
pop in:Perennial plant.

Size:6 to 10 in (15 to 25 cm) tall.
How to identify:Blue violet has glossy, heart-shaped leaves with purple flowers and white throats.
Notably, the lower three petals are hairy, and the flowers stem tends to droop slightly.
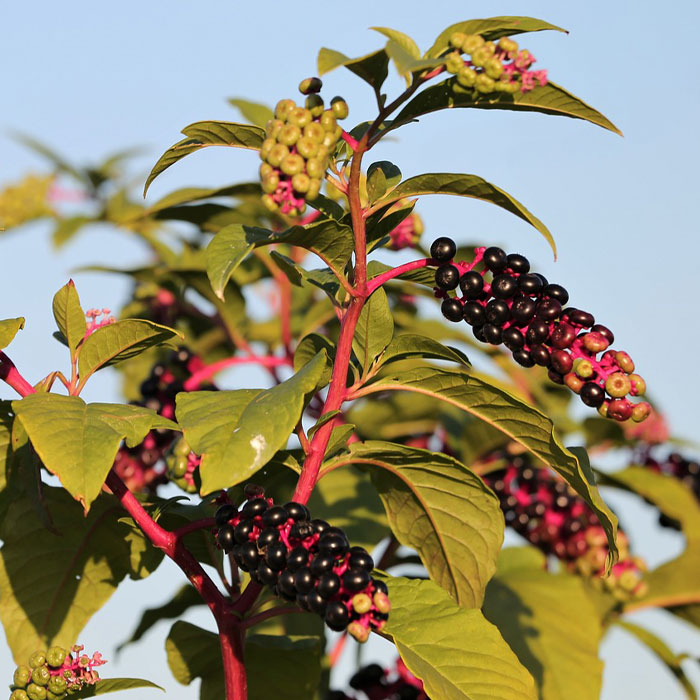

Due to its weedy nature, common blue violet is hard to control.
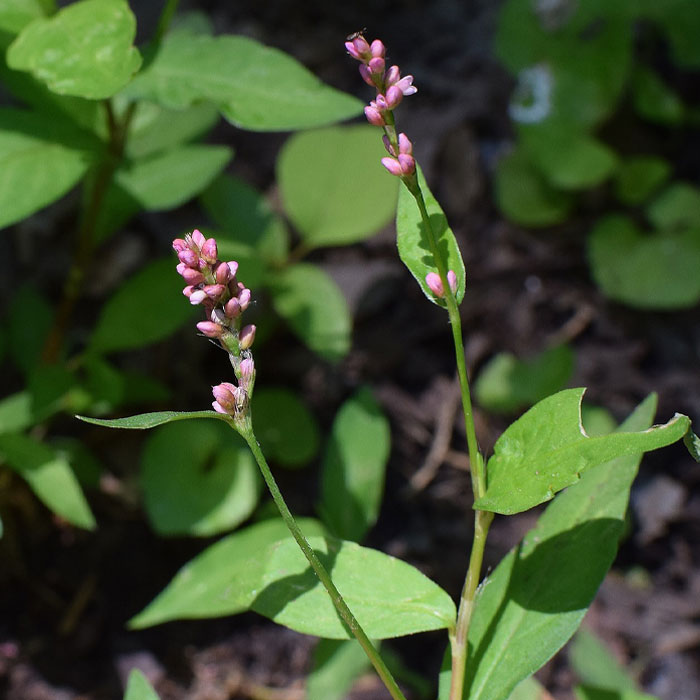
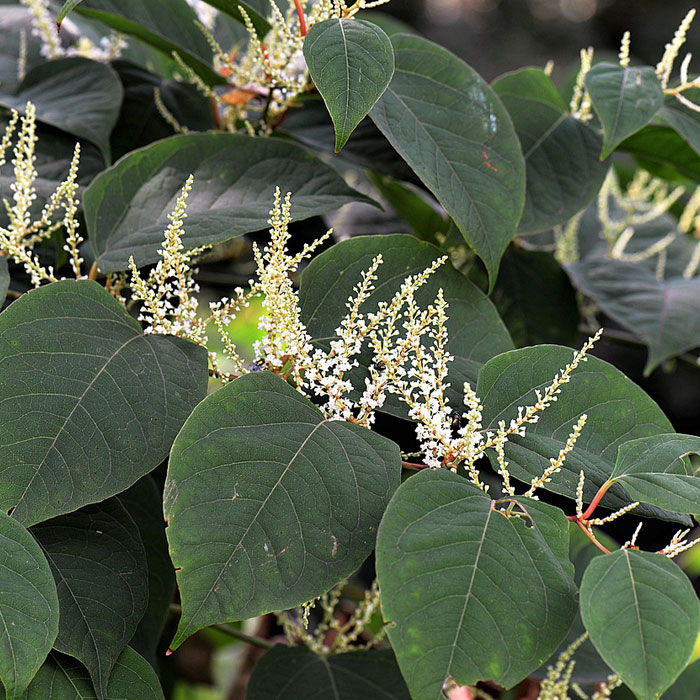
How to identify:The plant has tall, ribbed stems and lance-shaped leaves that often have dark blotches.
This weed produces many seeds that can persist in the soil for years.
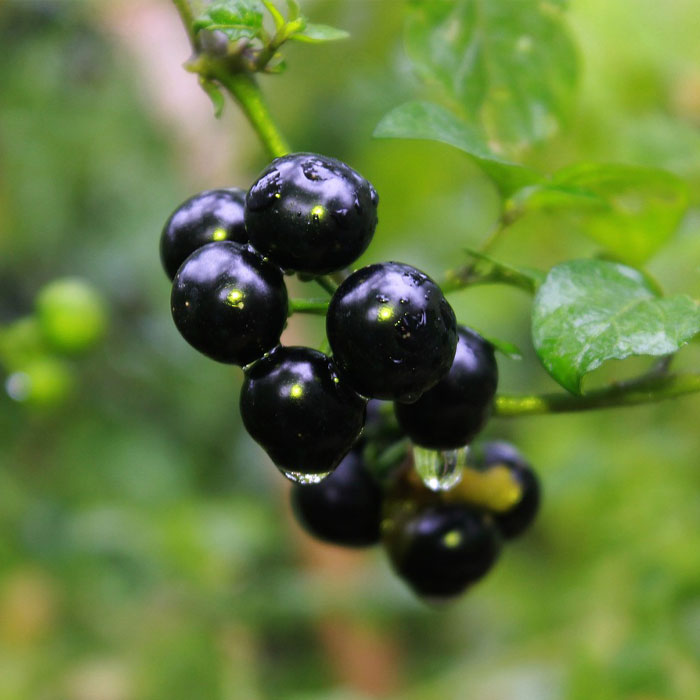

Therefore, its advisable to control it before it sets seeds and spreads.
Cover the affected area with mulch or plastic to prevent seed germination.
The leaves are opposite, oval, and toothed.

Cover the affected area with mulch or plastic to prevent the seeds from sprouting.
Consider using pre-emergentherbicides with active ingredients such asindaziflam, 2,4-D, orglyphosate.
Size:Usually 6 to 10 ft (1.8 to 3 m) tall.

It produces small, white flowers arranged in long, hanging clusters.
At first green, later purpleberries are poisonous.
American pokeweed istoxicto both humans and animals; thus, controlling its growth is very important.

Alternatively, you might use non-selective herbicides with the active ingredientglyphosateor selective broadleaf herbicides containingtriclopyr.
Size:1 to 3.9 ft (30 to 119 cm) tall.
The berries are green when unripe and black or purple when ripe.

Use pre-emergence herbicides with the active ingredientdithiopyrand post-emergent herbicides withquincloracduring crop destruction to minimize seed production.
just note that some nightshade biotypes have developed herbicide resistance.
#19 Black Medic(Medicago lupulina)
jot down:Annual or short-lived perennial weed.

Size:up to 20 in (0.5 m) tall.
Toothed stipules are present at the petiole bases.
The flowers eventually turn into black seed pods.

The leaves typically have three leaflets, but the form can vary.
Mature plants will produce flowers and waxy fruits.
The plant is invasive and poisonous andcan cause a harsh skin rash if touched.

To stop its growth, cut the vine and immediately apply a non-selective herbicide containingglyphosateortriclopyrdirectly to the cut end.
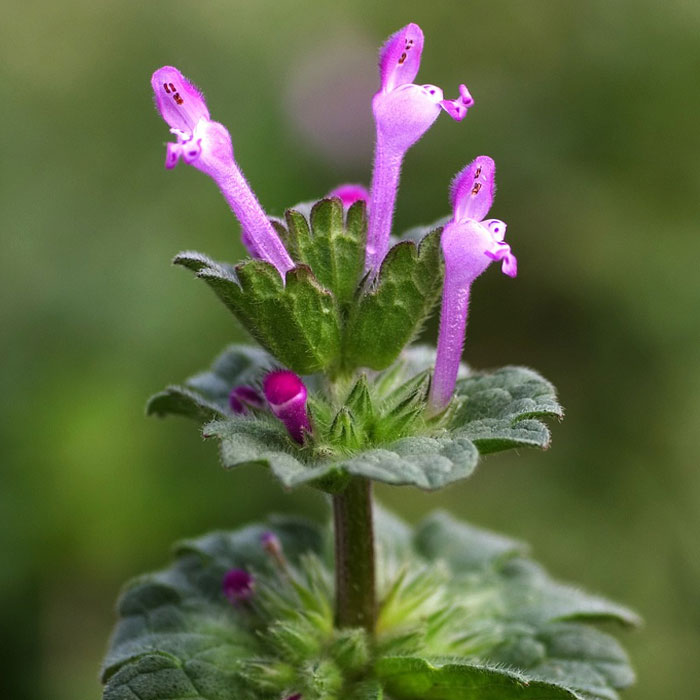
The lower leaves have petioles, while the upper leaves only half encircle the stem.
The pinkish-purple, lipped flowers grow in whorls in the axils of the upper leaves.

Common henbit should be controlled before it becomes a problem.
In the spring, use hand-pulling before the plants flower and produce seeds.
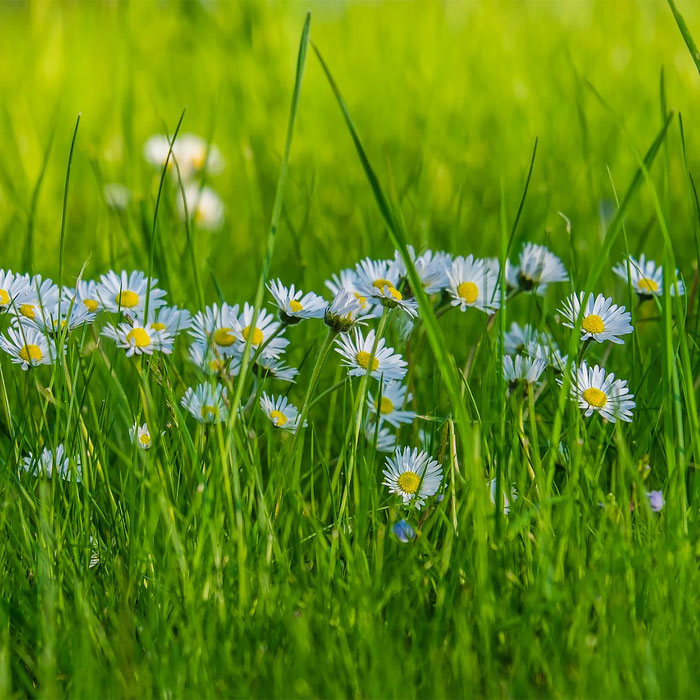
Size:8 in (20 cm) tall.
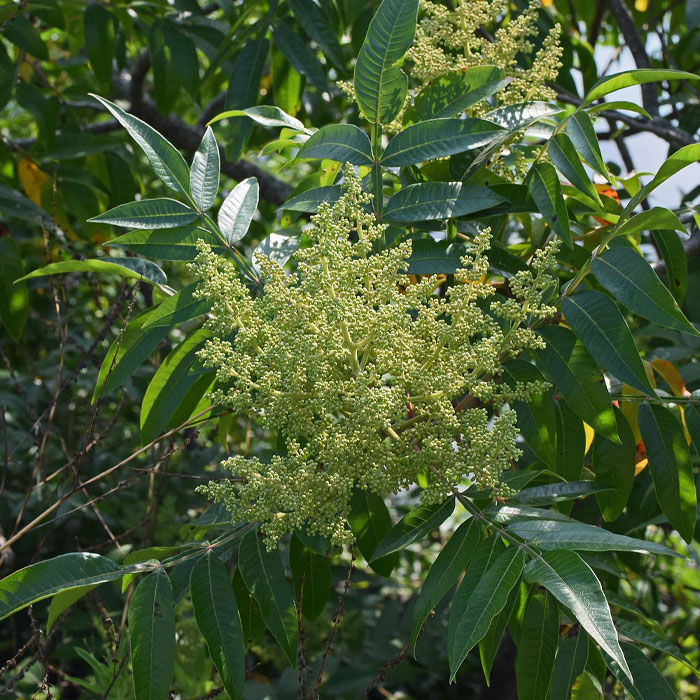

The flowers close at night and re-open in the morning, following the sun.
Common daisy is quite attractive in its flowering stage and is often preferred for cultivation.
However, if you still want to control its growth, focus on improving turf density.

Size:10 to 13 ft (3 to 4 m) tall.
It produces greenish, triangular-shaped fruits.
Cut and remove as much of the plants root as possible.

Keep removing any regrowth for several seasons.
After eight weeks following cutting, apply a non-selective herbicide containingglyphosate.
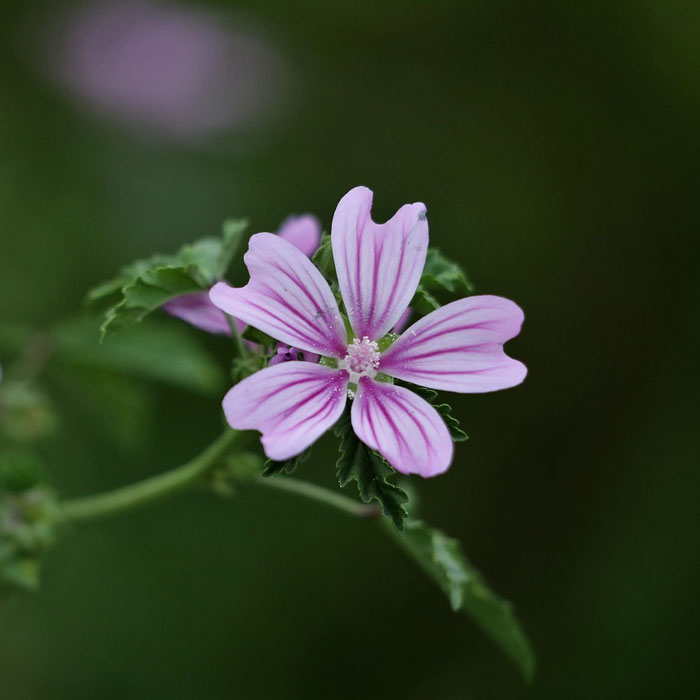
#24 Common Mallow(Malva neglecta)
bang out:Annual or biennial weed.

Size:Up to 1 ft (30 cm) tall.
The leaves are round in shape and hairy.
To control common mallow, maintain healthy, dense turf.

Use hand-pulling or selective post-emergent broadleaf weed herbicides containing2, 4-D, MCPP, dicamba, or triclopyr.
Size:6 to 8 in (15 to 20 cm) tall.
How to identify:The plant has a fibrous rootstock and a flattened stem.
The leaves are vivid green, canoe-shaped.
The flowers are in open, triangular panicles with stalked, awnless spikelets.
Annual bluegrass is pervasive in lawns, gardens, cultivated crops, and open spaces.

Its rapid growth in lawns outpaces other grasses, resulting in unsightly brown spots upon maturity.
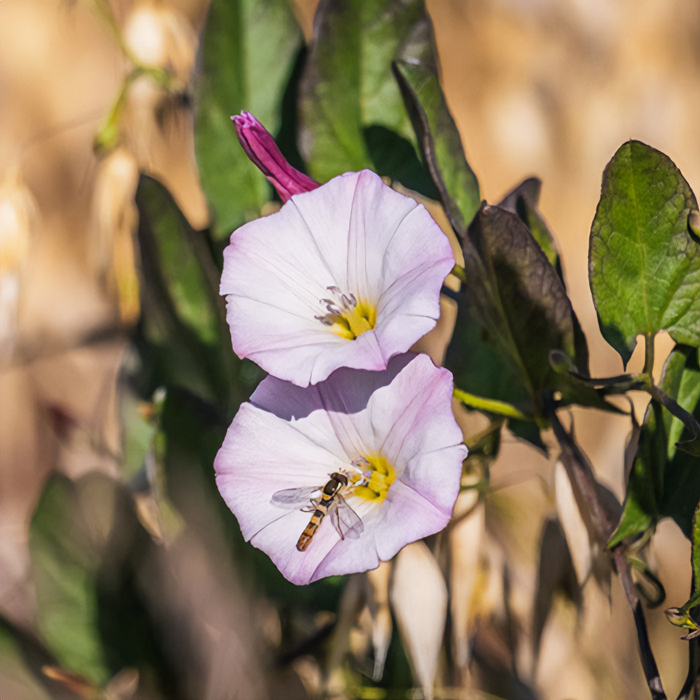
#26 Hedge Bindweed(Calystegia sepium)
jot down:Herbaceous perennial vine.
Size:Up to 10 ft (3 m) long.
Its leaves are arrow-shaped, smooth, and serrated at the edges.
This vine is beautiful and fragrant.
However, its also invasive and problematic for home gardeners.
Remove this bang out of weed by digging it up as soon as possible after germination.
#27 Poison Sumac(Toxicodendron vernix)
bang out:Perennial woody shrub or tree.
Size:Up to 30 ft (9 m) tall.
How to identify:The plant has pinnate leaves with 713 oval leaflets with serrated and wavy edges.
The leaflets are red along the stems.
The green flowers grow in clusters, followed by whitish-gray, flattened fruits.
All parts of the plant are toxicand can cause harsh allergies if touched or inhaled.
Pull out the plants by hand or with a hoe, ensuring you remove the entire root system.
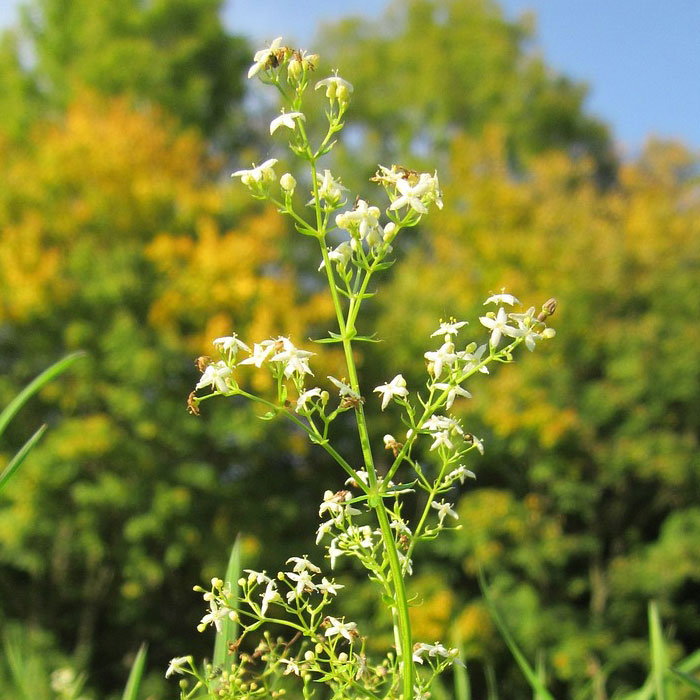
How to identify:Hedge bedstraw boasts square stems that stand upright with branches growing upward.
It produces small white flowers with four petals rising from the leaf axils.
Use effective tillage to destroy the perennial crowns and non-selective broadleaf herbicides to kill the unwanted plants.
Apply these methods in the spring before the plants flower and produce seeds.
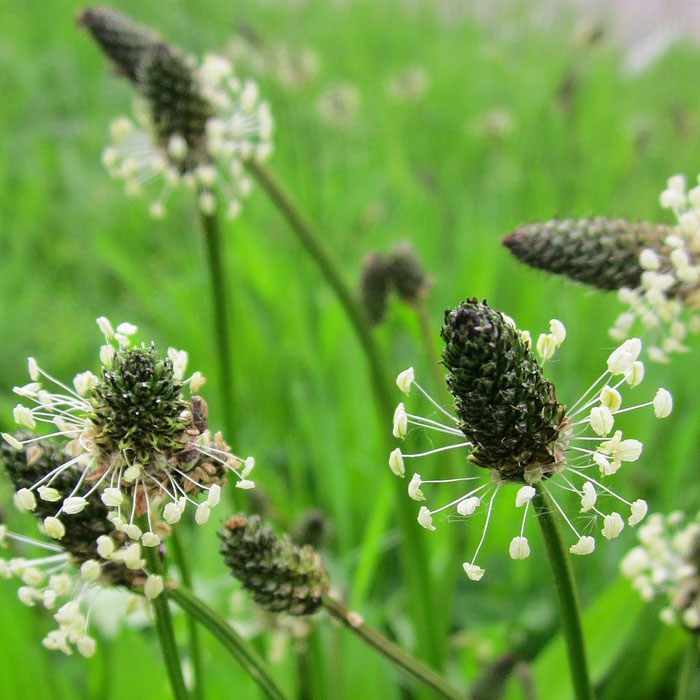
#29 Ribwort Plantain(Plantago lanceolata)
bang out:Herbaceous perennial.
Size:7 to 24 in (20 to 60 cm) tall.
Its distinguished by brown fruits positioned near the top of the stem.
Hand-pull plants before they produce seeds.
To limit the growth of seedlings, use pre-emergence herbicides containingisoxaben, flumioxazin,andindaziflam.
For established ornamental plantings, use post-emergence spot treatment with non-selective herbicides containingglyphosate.
How to identify:The plant is a fern that has two types of stems: fertile and sterile.
The fertile stems are brown, unbranched, and have cone-like structures at the tip that produce spores.
In contrast, the sterile stems are green, branched, and have whorls of needle-like leaves.
The stems are hollow and have joints that can be easily separated.
Common horsetail can be challenging to eradicate due to its deep and extensive rhizomes that can regenerate new plants.
Consider using a pre-emergent herbicide with the active ingredientdichlobenilor a post-emergent herbicide containingMCPAto control these types of weeds.
PopularQueries AboutLawn Weeds(FAQ)
How Do I Identify Weeds in My Plants?
There are several ways to identify weeds in the grass.
One of the easiest ways is to identify weeds by photo using this article or dedicated apps.
Here are some general tips for identifying weeds:
Does Vinegar Kill Weeds?
Vinegar can kill weeds by breaking down their cell walls and removing moisture.
However, vinegar isnt selective and will harm your desired plants if you spray them.
Therefore, you should use vinegar carefully and only on the weeds you want to get rid of.
On a sunny day, spray the vinegar solution on the leaves and stems of the weeds.
double-check you dont spray the soil or other plants.
You may need to reapply the solution every 23 days until the weeds die.